WebAssembly (WASM) in Blockchain: How It Enhances Smart Contract Security and Performance
I still remember the first time I saw a slow contract fail during a token launch. The gas spiked. Transactions stalled. People lost money and trust. That day I realized speed and security aren’t optional. They shape real lives.
WebAssembly is one of the tools changing that. It’s not magic. It’s a simple, efficient way to run code. When blockchains use WASM, smart contracts can run faster, safer, and in more languages than before. Now let’s see what it means.
WebAssembly: a simple explanation
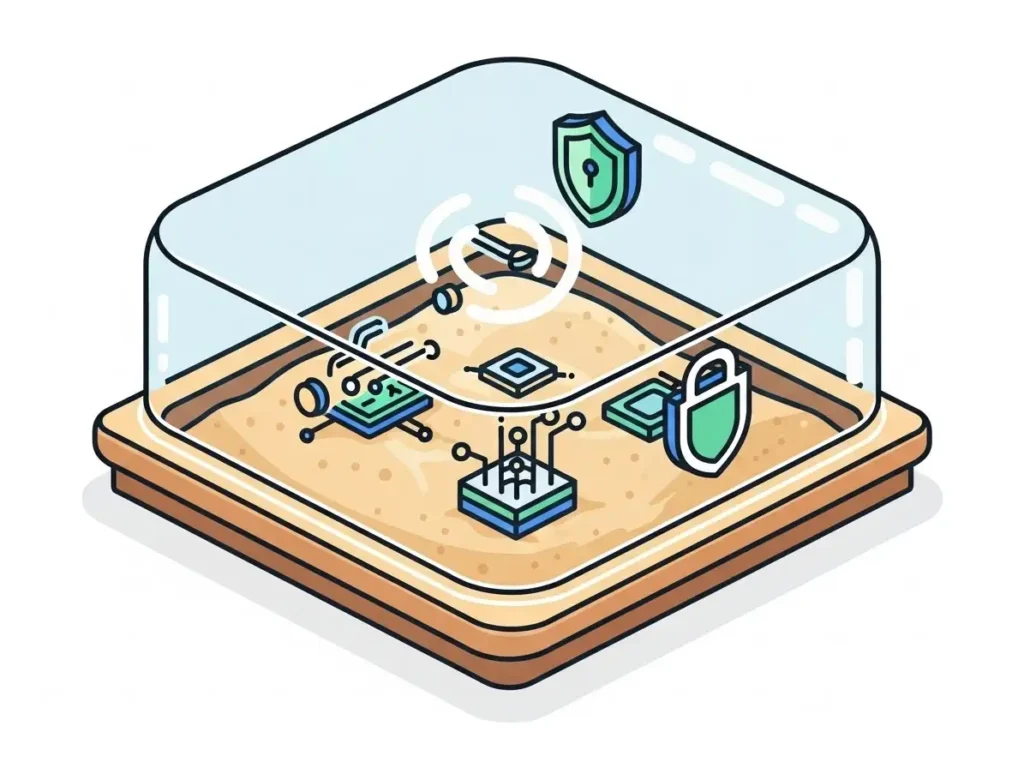
WebAssembly (often called WASM) started as a web technology. It lets websites run fast code written in languages like Rust, C, or Go. Think of WASM as a compact and quick middle language. Programs are compiled (converted) into WASM and then run inside a safe box, called a sandbox.
In blockchain, WASM plays the same role. Developers write smart contracts in familiar languages. Those contracts are turned into WASM. Nodes then run the WASM code in a sandbox. The result is code that is portable, quicker, and easier to audit.
Why blockchains adopted WASM
Blockchains used to rely mostly on their own virtual machines. Ethereum, for example, uses the EVM — a custom environment with its own rules. EVM works, but it has limits. It favors one language (Solidity) and can be slower to evolve.
WASM changes that:
- Language choice: You can code contracts in Rust, C, C++, Go, and more.
- Performance: WASM runs close to native speed. It uses modern compiler optimizations.
- Portability: The same WASM module runs across different blockchains with WASM support.
- Security: The sandbox limits what contract code can do on the host machine.
Those points explain why projects like Polkadot, NEAR, EOS, and several layer-2 solutions embraced WASM.
How WASM improves smart contract security
Security is the central reason many developers move to WASM. Here’s why, in plain terms:
Sandboxed execution
WASM runs inside a sandbox. Picture a sealed room where the code can work but cannot touch the building’s wiring. That room prevents direct access to the host system. Even if a contract has a bug, the damage is limited.
Deterministic behavior
Blockchains need predictable results. Every node running the same input must produce the same output. WASM supports deterministic execution when properly configured. That reduces nasty surprises caused by language or runtime differences.
Smaller trusted codebase
WASM engines are usually compact and well-audited. With fewer moving parts, there’s less to go wrong. Fewer bugs in the runtime mean stronger trust in contract execution.
Safer memory model
WASM uses linear memory with bounds checks. That means buffer overflows and many memory bugs common in lower-level languages are harder to exploit. The runtime enforces limits.
Easier auditing
Contracts compiled to WASM have clear structure. Tools can analyze the bytecode to find patterns or suspicious behavior. While not trivial, static analysis and formal tools work well on WASM modules.
How WASM boosts performance

Speed matters. Faster contracts mean cheaper gas per operation and better user experience.
Near-native speed
WASM is designed to be compiled to native machine instructions efficiently. That gives it a speed advantage over older interpreters.
JIT and AOT options
WASM engines support Just-In-Time (JIT) and Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation. Nodes can compile hot code paths to machine code for repeated use. That saves time on heavy workloads.
Compact code size
WASM binaries are compact. Smaller size means faster propagation between nodes and quicker deployment.
Better tooling for optimization
Modern language toolchains (Rust, LLVM) include advanced optimizers. Compiled WASM benefits from these tools and becomes faster.
Real-world examples and use cases
Here are simple examples showing where WASM helps.
1. DeFi order matching
A decentralized exchange needs to match many orders quickly. Faster smart contract logic means higher throughput and fewer stuck trades. WASM’s speed helps here.
2. NFTs with complex logic
NFT minting with on-chain metadata or royalties can be heavier than simple transfers. WASM lets creators write more expressive contracts without blowing up gas costs.
3. Cross-chain modules
Projects building parachains or sidechains often need portable modules. WASM allows the same compiled contract to run in multiple environments, easing migration.
Development experience
WASM opens doors to more developers.
Use familiar languages
Not everyone wants to learn Solidity. Rust or Go developers can write contracts in languages they already know. That makes blockchain development more inclusive.
Better debugging tools
Rust and other ecosystems have mature debugging and testing tools. Developers can run unit tests locally before compiling to WASM.
Reuse existing libraries
Many non-blockchain libraries can be compiled to WASM and reused, reducing repeated work. But be careful with dependencies — always review what the compiled code includes.
Security trade-offs and pitfalls
WASM improves many things, but it isn’t a silver bullet. Watch out for these issues.
Determinism must be enforced
WASM itself does not guarantee deterministic performance. Blockchains must restrict features like floating-point non-determinism, certain syscalls, and external randomness. Protocol rules must enforce determinism.
Attack surface shifts
While WASM’s runtime is smaller, format complexity and compiler bugs can introduce risks. Compiler toolchains are large; supply-chain attacks or compiler bugs can slip in. Vet your toolchain.
Gas and metering complexities
WASM code can be more expressive and complex. Blockchains must meter execution carefully to avoid denial-of-service attacks. Designing fair gas models for WASM takes care.
Unsafe host calls
Contracts often call host functions (like reading a block timestamp). If host functions are poorly designed, contracts can get unpredictable or leaked data. Keep host APIs minimal and auditable.
Best practices for developers and operators
If you plan to use WebAssembly for smart contracts, these practical tips help:
For developers
- Write tests that run on local WASM runtimes.
- Keep contracts small and focused.
- Avoid unnecessary third-party dependencies.
- Prefer languages with strong tooling (Rust is a common choice).
- Use formal verification or static analyzers when possible.
For node operators and protocol designers
- Limit host functions and document them clearly.
- Enforce deterministic compilation flags.
- Implement strict gas metering for WASM opcodes.
- Keep the WASM engine updated and audited.
- Offer proof-of-reserves or verification tools for runtime integrity.
Tooling and ecosystem
WASM benefits from a broad ecosystem. Key tools include:
- Wasm-bindgen and wasm-pack for Rust.
- LLVM for compiling C/C++ to WASM.
- Standalone WASM runtimes like Wasmtime, Wasmer, and WAVM.
- Blockchain-specific SDKs: Substrate (Polkadot), NEAR SDK, CosmWasm (for Cosmos).
These tools make the developer experience smoother and help teams ship safer code.
Adoption and future outlook
WASM is already in use in production blockchains. Adoption is likely to grow because it solves real pain points: performance, language choice, and security. Expect to see:
- More developer toolchains.
- Standardized host APIs to avoid fragmentation.
- Enhanced formal verification methods for compiled WASM.
- Tighter integrations between wallets, dev tools, and WASM runtimes.
Over time, WASM may become a universal contract format across multiple chains, making cross-chain tooling simpler.
Conclusion
WebAssembly brings practical improvements to smart contracts. It speeds execution, widens language options, and strengthens security through sandboxing and a smaller runtime. That said, success depends on careful choices: deterministic rules, secure host APIs, strict metering, and trusted toolchains.
If you are a developer, WASM means new languages and better tools. If you run a node or design a protocol, WASM asks you to think about metering, APIs, and audits. For users, it means faster, safer interactions — when projects do the work right.
In short: WASM is an important step forward. It doesn’t solve every problem, but it gives developers and architects better building blocks. The result is smarter, faster, and more secure contracts — and that is worth writing about.
Summary
- WebAssembly (WASM) is a compact, fast format for running code.
- WASM brings language flexibility: Rust, C, Go and more.
- Sandboxing improves security by limiting what contracts can do.
- WASM often runs faster than older virtual machines.
- Determinism and gas metering are essential to safe WASM use.
- Watch for toolchain and compiler risks; audit frequently.
- Use small contracts, strong tests, and minimal host APIs.
- WASM is already used in many blockchains and is growing.
FAQ
Q: Is WASM safer than EVM?
A: WASM offers sandboxing and modern tooling that can improve safety, but final security depends on runtime configuration, deterministic rules, and audits. It’s safer if implemented carefully.
Q: Which languages can I use with WASM?
A: Common choices are Rust, C, C++, and Go. Rust is popular for its safety features and tooling.
Q: Will my WASM contract run on any blockchain?
A: Not automatically. Chains must support the same WASM host APIs and deterministic rules. Portability improves as standards converge.
Q: How does gas metering work with WASM?
A: Chains measure WASM instruction costs and charge gas accordingly. Designing fair and attack-resistant metering is an active area of research.
Q: Can existing Solidity contracts be moved to WASM?
A: Directly no. Solidity targets the EVM. Porting requires rewriting or compiling from a supported language into WASM, or using cross-compilers that translate EVM bytecode with caution.

Hello, I’m Edmilson Dias, founder of CoinBringer. I created this platform to guide people through the fast-moving world of cryptocurrency with clarity and safety. With years of research in blockchain and digital security, my goal is to translate complex topics into practical knowledge, offering reliable tutorials, safety insights, and guidance for both newcomers and experienced users.
Discover more from CoinBringer
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.