Wallet Monitoring: How to Set Up Real-Time Alerts for Suspicious Activity
Ok, I want to start with something honest: losing crypto can feel awful. It’s like watching a small plant you’ve cared for disappear while you stand there with your hands in your pockets. People who’ve lost money to a bad transfer or a sneaky approval tell the same story — a quick message, a panic, and a moment they wish they could rewind.
Wallet Monitoring helps you avoid that “I wish I’d known sooner” feeling. It is a set of tools and rules that watch one or more crypto addresses and send you a live alert when something odd happens. Think of it as a smoke detector for your wallet: it won’t stop the fire, but it will warn you in time to act.
What is Wallet Monitoring and why it matters
Well, Wallet Monitoring is simply watching your wallet address on the blockchain for activity you care about. This includes outgoing transfers, approvals given to apps, sudden drops in balance, or transactions that look strange.
Why does this matter? Because once a transaction is confirmed on most blockchains, it can’t be undone. If someone gets control of your keys or tricks you into approving a malicious contract, the faster you know, the better your chance to react.
A real alert delivered minutes before a transfer can let you pause, call support, or move funds. It gives you a fighting chance.
Who should use wallet monitoring?
- Casual holders who want peace of mind.
- Traders with funds on multiple addresses.
- NFT collectors worried about accidental sales or approvals.
- Small exchanges, DAOs, or teams that manage shared funds.
Even if you hold a small amount, bad luck can happen. A single phishing link or a wrongly approved contract can drain money fast. Monitoring is simple and often inexpensive.
Types of alerts you can set
Here are common triggers people use. I’ll explain them plainly.
Outgoing transaction
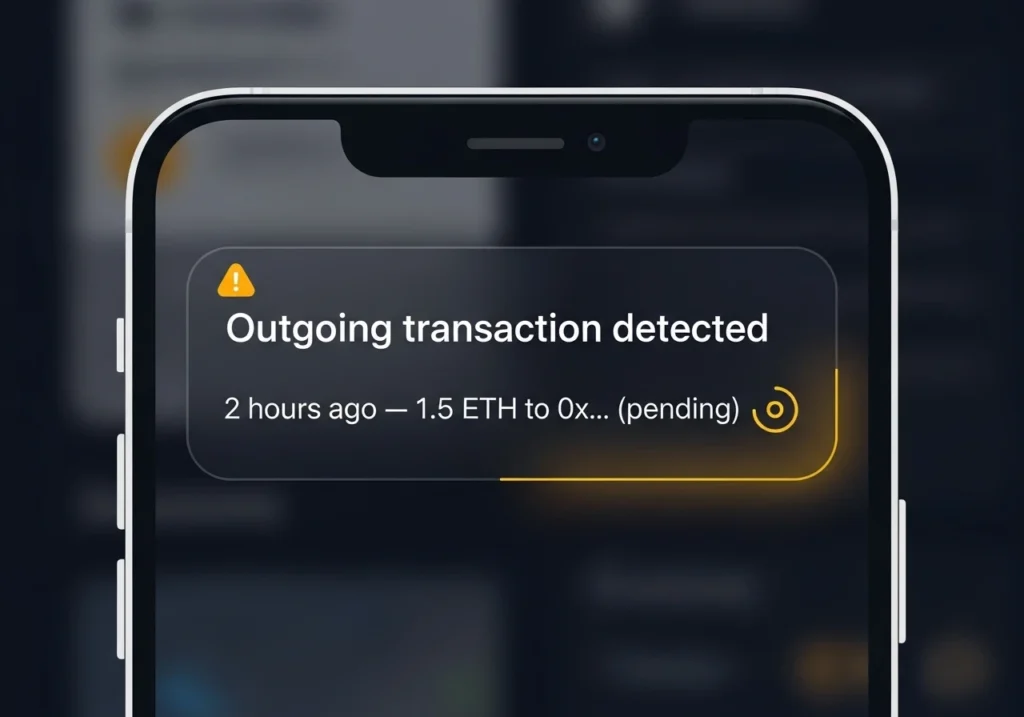
Alert when any funds leave the address. If you see money move out and you didn’t send it, that’s a red flag.
Large transfer threshold
Only alert if more than a set amount (for example $100 or 1 ETH) leaves. Good for noisy wallets with many tiny transfers.
New token received
Notify when your wallet receives a new token or airdrop. This is useful because attackers sometimes send strange tokens to trick you into interacting.
Contract approvals
Alert when you or someone else approves a contract to spend tokens on behalf of your wallet. Approvals are a common entry point for thieves.
Balance change
Watch for sudden drops in total value. This looks at all assets in your wallet and warns if the value falls quickly.
Suspicious contract interaction
Flag when your wallet interacts with a contract with known bad indicators — for instance, a contract flagged by community databases.
Pending mempool activity
Some advanced services watch the mempool (the pending queue) and can let you know if a transaction from your address is about to be confirmed. This gives extra seconds to act.
How to choose a wallet monitoring service
You have options. I’ll name types without pushing specific brands.
1. Exchange or wallet native alerts
Many custodial wallets and exchanges already offer notifications. These are easy to use but only work while your funds are held with them.
Good if: You keep funds on an exchange and want basic alerts.
2. Third-party monitoring services
These services let you add any public address and choose alerts. They send messages by email, SMS, Messenger, Telegram, or webhooks.
Good if: You use several wallets or want richer alert types like approvals and mempool watches.
3. Self-hosted scripts and nodes
If you or your team are technical, you can run your own node or script to watch addresses and trigger alerts. This is the most private option.
Good if: You care about privacy and control and can manage servers.
4. Hybrid
Use a service for monitoring and set up local scripts for sensitive checks. This mixes convenience and control.
Good if: You want balance between ease and privacy.
Step-by-step: setting up real-time alerts
I’ll show a plain, practical setup using a third-party service. The names and buttons may differ by provider, but the steps are similar.
Step 1 — Prepare your address
Find the public address you want to monitor. It’s the string you share to receive crypto. Do not share your seed phrase or private key with anyone. Sound obvious, but it happens.
Step 2 — Sign up for a monitoring account
Create an account with a monitoring provider you trust. Use a unique password and enable two-factor authentication.
Step 3 — Add the address
Enter the public address into the dashboard. You can add multiple addresses: individual wallets, smart contracts, or a group wallet.
Step 4 — Choose triggers
Select the alerts you want: outgoing tx, approvals, large transfers, etc. Set amounts and thresholds. If you hold multiple assets, choose a total value change alert too.
Step 5 — Choose notification channels
Pick where alerts go: email, push notification, Telegram, SMS, or webhook to a Slack channel. Use more than one channel if you can. If your phone number is at risk (SIM swap), prefer app push or encrypted channels.
Step 6 — Test the system
Most services let you send a test alert. Use that. Then try a small, safe transaction from a test wallet to see the alert flow.
Step 7 — Build a response plan
Decide exactly what you will do when an alert arrives. Who calls whom? Which steps to take? Write it down.
What to do when an alert fires
An alert creates options. It does not stop the blockchain. Here is a short playbook.
If you see an outgoing tx you didn’t authorize
- Check if transaction is pending. If yes, try to speed up or cancel via replacement (advanced).
- Move unaffected funds to a cold wallet if you can.
- Revoke approvals using a tool (if you can sign transactions and the funds remain).
- Contact exchange support if funds were on an exchange.
- Post to trusted community channels for help only after verifying facts.
If you see a suspicious approval
- Revoke the approval immediately if you have access.
- Move tokens to a new address if approvals were broad.
If you see a small odd transfer
- Be cautious. Some scams start with tiny tokens or messages. Don’t click links or sign transactions unless you know the source.
Important: act calmly. Quick reactions help, but hasty mistakes can worsen things.
Practical safety tips to pair with monitoring
Monitoring is not a cure on its own. Pair it with solid habits.
- Use hardware wallets for high-value funds. They make unauthorized transactions harder.
- Don’t share your seed phrase. Ever.
- Use multi-signature wallets for shared funds — this prevents a single compromised key from draining assets.
- Revoke unused approvals regularly.
- Avoid using SMS for critical notifications if you can (SIM swap risk). Use authenticator apps or push notifications.
- Keep one small “hot” wallet for daily use and a secure “cold” wallet for savings.
Privacy and security concerns
Monitoring requires you to share public addresses. Those addresses are already public on the blockchain, so monitoring does not add exposure there. However, linking different addresses to your identity can be a risk.
- Do not publish the whole monitoring dashboard publicly.
- Use separate addresses for different activities if privacy matters.
- Choose providers with good privacy policies. Prefer ones that don’t require full KYC unless necessary.
Example: a simple scenario
Emma collects NFTs and keeps some tokens in a wallet. She wants a simple plan.
- She signs up with a monitoring service.
- She adds her NFT wallet address.
- She sets alerts for: any outgoing transaction, any approval, and a balance drop > 20%.
- She chooses push notifications and email.
- A week later she gets an alert: a pending approval to a contract she doesn’t recognise. She revokes the approval and checks her seed. All good — a potential scam was avoided.
That heads-up saved her a lot of worry.
Cost and complexity
Many services offer free tiers. Paid plans add advanced features like mempool watching, webhook support, and more addresses. Self-hosting costs vary — you might run a small server for modest fees.
Pick what fits your needs. For many users, a simple free service plus a hardware wallet is enough.
Final thoughts: small steps, big peace of mind
Setting up Wallet Monitoring is not hard. It is a practical step that turns uncertainty into control. You do not need to be a coder or a millionaire to use alerts. A little setup today can save you hours of panic later.
Think of monitoring as a friendly neighbor who checks your mailbox and calls if something looks wrong. That small heads-up can keep your crypto right as rain.
Key takeaways
- Wallet Monitoring watches public addresses and sends real-time alerts.
- Common triggers: outgoing tx, large transfers, contract approvals, balance drops.
- Use trusted providers, but never share private keys or seeds.
- Combine alerts with hardware wallets and multi-sig for best protection.
- Test alerts and have a response plan ready.
- Prefer secure notification channels over SMS when possible.
- Monitoring is affordable and gives practical peace of mind.
FAQ
Q: Will wallet monitoring stop a thief?
A: No. It cannot stop an on-chain transaction once confirmed. But it can alert you fast, giving you options to respond (revoke approvals, move funds, contact support).
Q: Can a monitoring service see my funds?
A: They can see the public activity of the addresses you add, which is already publicly visible on the blockchain. They should not ask for private keys or seeds.
Q: Is SMS safe for alerts?
A: SMS is convenient but vulnerable to SIM swap attacks. Use app push notifications or encrypted messages when possible.
Q: Can I monitor multiple blockchains?
A: Many services support multiple chains. Make sure the provider supports the specific blockchain and token types you use.
Q: How much does it cost?
A: Many basic services are free. Paid plans add features like mempool watching, webhooks, and more addresses. Self-hosting may have server costs.

Hello, I’m Edmilson Dias, founder of CoinBringer. I created this platform to guide people through the fast-moving world of cryptocurrency with clarity and safety. With years of research in blockchain and digital security, my goal is to translate complex topics into practical knowledge, offering reliable tutorials, safety insights, and guidance for both newcomers and experienced users.
Discover more from CoinBringer
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.